Eps 1111: Fuel cell
— The too lazy to register an account podcast
In this type of fuel cell, the membrane must be hydrated, requiring water to be evaporated at precisely the same rate that it is produced.
The energy efficiency of a system or device that converts energy is measured by the ratio of the amount of useful energy put out by the system ("output energy") to the total amount of energy that is put in ("input energy") or by useful output energy as a percentage of the total input energy.
In the case of fuel cells, useful output energy is measured in electrical energy produced by the system.
Host

Charlie Harris
Podcast Content
Different types of fuel cells are mainly based on the type of electrolyte used by the fuel cell. The FCEVs are powered by pure hydrogen gas stored in the vehicle's tank and use an electrochemical process in which the energy stored as hydrogen is converted into electricity by a fuel cell. Fuel cells have two main components: hydrogen fuel and oxidant, or the chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen.
It has a range of up to 300 miles and is powered by a hydrogen fuel cell with a capacity of 1,000 kilowatt hours per year.
FCEVs are equipped with other advanced technologies to increase efficiency, such as a regenerative braking system that absorbs lost energy during braking and stores it in the battery. A fuel cell, on the other hand, can mix hydrogen with air to produce electricity with 60 percent efficiency. Compared to less efficient electric batteries, today's fuel cells are relatively cheap.
FCEVs are a relatively low entry barrier that works well enough to refuel at a station and travel up to 15 kilometers on a single charge in minutes, according to the US Department of Energy. Fuel cell vehicles may drive if electricity comes from renewable sources such as wind, solar, geothermal, hydroelectric or hydrofluorocarbons. This offers the potential for higher efficiency and lower operating costs, as well as more efficient fuel consumption.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are similar to electric vehicles in that they use hydrogen fuel cells and / or other renewable energy sources to drive the wheels. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles are similar in that they need to be connected, but they also have a conventional petrol or diesel engine. Unlike fuel cell cars and trucks, battery electric vehicles can use existing infrastructure to recharge themselves.
Electric vehicles run on batteries that need to be connected to recharge, electric vehicles can generate their electricity from a plug - in hybrid or hybrid vehicles.
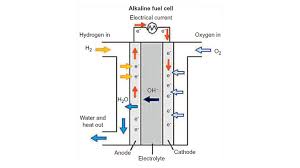
Fuel cells are electrochemical devices that combine hydrogen fuel with oxygen to generate electricity and heat for water. In a fuel cell, oxygen and air are combined to generate electricity, with only water heat being produced as a by-product of the process. Fuel cell is an electrochemical device that combines hydrogen with oxygen and generates electricity or heat .
Hydrogen is stored in a pressure vessel, oxygen is removed from the air and the only product is pure water. Fuel cells are similar to batteries because the electrochemical reaction takes place as long as fuel is available. Without combustion, no harmful emissions are produced; the fuel cell converts fuel into electricity and heat.
Natural gas consists mainly of methane and CH 4, while hydrogen must be separated from the carbon used in the fuel cell. The amount of water from fuel cells is collected and fed to the reformer, which recycles the steam and methane heated by the reforming process. The resulting hydrogen is then fed into the fuel cell and the other gases are ventilated.
Fuel cells are energy efficient because they generate electricity chemically instead of by combustion. This is an energy conversion technology that absorbs the chemical energy contained in the fuel and converts it into electricity or a specific product, depending on the fuel used.
However, it is important to note that fuel cells are not heat machines, so they can have incredibly high efficiencies. When a heat engine is used to drive a fuel cell, it has limited thermal efficiency, but not as much as an internal combustion engine.
A fuel cell uses the chemical energy of hydrogen fuel to generate electricity cleanly and efficiently. One can see from a fuel cell that energy is used to produce hydrogen and oxygen, which can remain in the cell until they are needed later.
Fuel cells are unique in that they can power a wide range of applications, including electric vehicles, power plants and industrial applications. Fuel cells can be used in a wide range of applications, including power generation, energy storage, fuel cell storage and energy distribution. SOFCs are used in everything from auxiliary power systems in vehicles to stationary power supply - generation with an output of 100 W / 2 MW.
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells, also known as Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells , offer high power density and have several advantages in terms of lower weight and volume compared to other FCs . They use a polymer membrane as an electrolyte with a porous carbon electrode containing a platinum catalyst. The high operating temperature makes the fuel cell more efficient than other fuel cells and further increases the overall fuel efficiency.