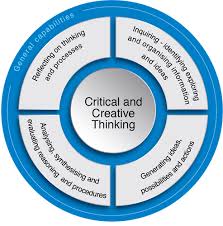
Eps 1: creativity and critical thinking
Creativity and critical thinking sit atop most lists of skills crucial for success in the 21st century.
Bloom's Taxonomy treats the two as separate educational goals, ranking creativity above critical thinking in the progression of intellectual abilities.
Critical analysis of historical problems often employs invention and is (or should be) rewarded for its creativity.
Host

Cody Olson
Podcast Content
When this kind of critical and creative thinking is practised frequently and with targeted content and teaching, content learning is promoted as a necessary skill. The ability to identify, analyze, and evaluate relevant data to provide an appropriate response to a problem is attributed to critical thinking and is used by leaders on a daily basis for effective decision-making. By researching opinions and expressing opinions or ideas, we develop the capacity to think about cause and effect, predict rational outcomes, and make judgments.
Now that computers are able to analyze and store information, they are able to use that data to develop creative solutions.
But when it comes to decision-making tasks, the human element of critical thinking is still necessary. If critical thinking is understood to include careful thinking on a subject for the purpose of its purpose, problem-solving and decision-making is a kind of "critical thinking," because it is carefully executed. But if critical thinking is narrowed down and consists exclusively of the evaluation of an intellectual product, it can be separated from the fact that it must be constructive and constructive.
Bloom's taxonomy of educational goals uses terms like "intellectual ability" and "skill" to characterize critical thinking, but not problem solving, decision-making, or creative thinking.
Clearly identify a set of teachable skills to define critical and creative thinking, assess your current knowledge on the subject, and mobilize the resources available. Applying the critical - creative - thought process to the attempt to define it is exciting and enables us to make progress in informing educators about how to develop it in their students. These so-called "higher order thinking skills" are not just critical thinking skills, though they come with their own challenges, such as the need to evaluate and evaluate.
Although creativity is often defined as generating many original ideas, we must also recognize that creative thinking involves selecting appropriate ideas to move forward. Creative and critical thinking, described by others in many ways as "creative" and "critical thinking," examines the ability to generate an idea to achieve a goal or to generate a large number of possible solutions.
While creative thinking can emphasize the generation of several original ideas, critical thinking also involves the generation of ideas. Moreover, the analysis, synthesis and evaluation of ideas is often seen as the crucial part of creative and critical thinking, not the creative part. Creative thinking could involve creating a single original idea, such as an idea for a new product or a solution to a problem, while critical thinking could emphasize the ability to make reflected judgments. Critical thinking, however, is also involved in the generations of the idea; however, it does not necessarily involve "idea generation," although it can emphasize abilities such as reflective judgments.
To encourage students to think about creative and critical thinking, any approach that can combine critical and creative thinking must be implemented, rather than focusing solely on these distinctions.
Julie notes that the advantage of critical thinking is that it can help students to find and evaluate information found in left hemisphere functions that have logical and analytical qualities.
Moreover, creative thinking also has the advantage that this kind of thinking can improve students "academic performance if they can recognize their creative abilities. To combine creative and critical thinking, one of the approaches that can help students is the application of problem solving techniques. Children can develop thinking skills by manipulating ideas, critically questioning them and trying to combine them in new ways.
Black refers to productive thinking, in which thinkers engage in activities that encourage them to take on previously acquired knowledge and transform the ideas into something that can be applied to new situations and problems. In order to advance cognitive development, challenge the status quo and require social action, talented students must be involved in the creation of new questions and the generation of innovative ideas, solutions and products. It is recognised that talented learners develop and practice basic information that is used in the development of cognitive skills such as critical thinking and critical analysis.
Thinking fluently and productively refers to the ability to generate a variety of ideas and concepts . The process of generating ideas is supported by thinkers who have a high level of language competence and a broad spectrum of cognitive abilities .