Eps 2: circuit composition
An electronic circuit can usually be categorized as an analog circuit , a digital circuit , or a mixed-signal circuit (a combination of analog circuits and digital circuits).
A circuit diagram representing an analog circuit, in this case a simple amplifier
The design process for digital circuits is fundamentally different from the process for analog circuits.
Host

Sheila Griffin
Podcast Content
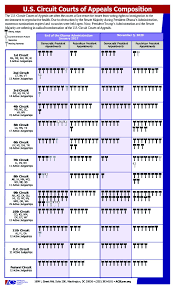
The court is divided into 13 districts, but its jurisdiction is not geographical, but the Federal Circuit has jurisdiction over the entire United States and the District of Columbia. Appeals are heard in federal and administrative courts, which are appointed by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit in Washington, D.C., and the Circuit Court in New York City.
The state's appeals courts have the power to set a legal precedent in regions that affect millions of Americans. Appeals by county courts are submitted to the United States Supreme Court for consideration by the US Congress, and are considered the highest court in the country and the nation's most important appeals court.
In 1948, the United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York was elevated to District Court status. In 1948, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 9th Circuit of the U.S. District Court of Appeals was elevated to the highest level of the federal appeals court, the Federal Court of Appeals.
In 1915, the Court of Appeals of Puerto Rico was assigned to the 1st District and the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of New York to its current status.
The US SS 43 provides that within each circuit there is a Court of Appeal known as the Court of Record, the United States Court of Appeals for that circuit. Currently, each of the three districts has two appellate courts, as approved by Congress. All other federal judges are nominated by the President of the United States and confirmed by the Senate.
This means that the 9th Circuit will have a political balance that has not been seen since the introduction of 10 rulings in the late 1970s. The actual number of judges on duty may vary because the higher judges who continue to hear cases are not counted against the number of empowered judges. If all current 9th Circuit nominees are confirmed, only one vacancy will remain.
Second, it means that the en banc panel, an 11-member super-panel that typically consists of randomly selected active judges, has the potential to form a conservative majority when Trump takes office and appoints a liberal majority.
En banc panels have extraordinary power to reshape the circuit law, as they can redecide the decision of a three-member panel and even override the precedents of the circuit's past. The majority of Republican appointees on the panel have created new opportunities to overturn flawed decisions and behave more conservatively than even the most conservative members of the panel.
On December 9, there were 48 judges appointed by President Trump to approve the Circuit Court's decisions, or more than one-third of the total number of judges in the United States.
The tenth circuit was established in 1929 and subdivided by the existing eighth circuit, and the eleventh circuit was created in 1981 by subdividing an existing fifth circuit. There was already a Republican-appointed majority of active judges on the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals. Confirmations reversed that, establishing a Republican majority and a Republican minority representative appointed by the President of the United States.
The Federal Circuit was created in 1982 and also handles certain claims filed in district courts, such as civil lawsuits against the US Department of Justice.
The Judiciary Act of 1789 established three circuits, which are jurisdictions established by the US courts. The district courts exercise the original jurisdiction of the district court within the district. Circuit courts consist of three separate courts, each with its own court district, and are not administered by itinerant judges who reach out to each other. There are three circuits, each judge being assigned to a group of circuits within each court and a district court.
When the Civil War began, the Supreme Court was dominated by Southern justices who had life-long appeals. Congress created circuits for new states as soon as they joined the Union.
With nine seats representing nine federal courts, Congress decided to redraw the boundaries of the county courts and reduce the five Southern Circuits to just two. To make this possible, Congress approved the 10th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals in March 1863. Lincoln nominated a new judge, John F. Kennedy, a member of the Supreme Court, to take on the role of chief justice of this new circuit, the 9th Circuit.
The Senate confirmed two of Kennedy's appointees to the 9th Circuit, Justice John F. Kennedy Jr., who left for California, and Justice William H. Roberts Jr. of the 9th Circuit. The New York Times, Justice Kim Bader Ginsburg and Justice Sonia Sotomayor noted that most of Trump's appointees were in the transition phase.